Basic Data stucture
list
list code
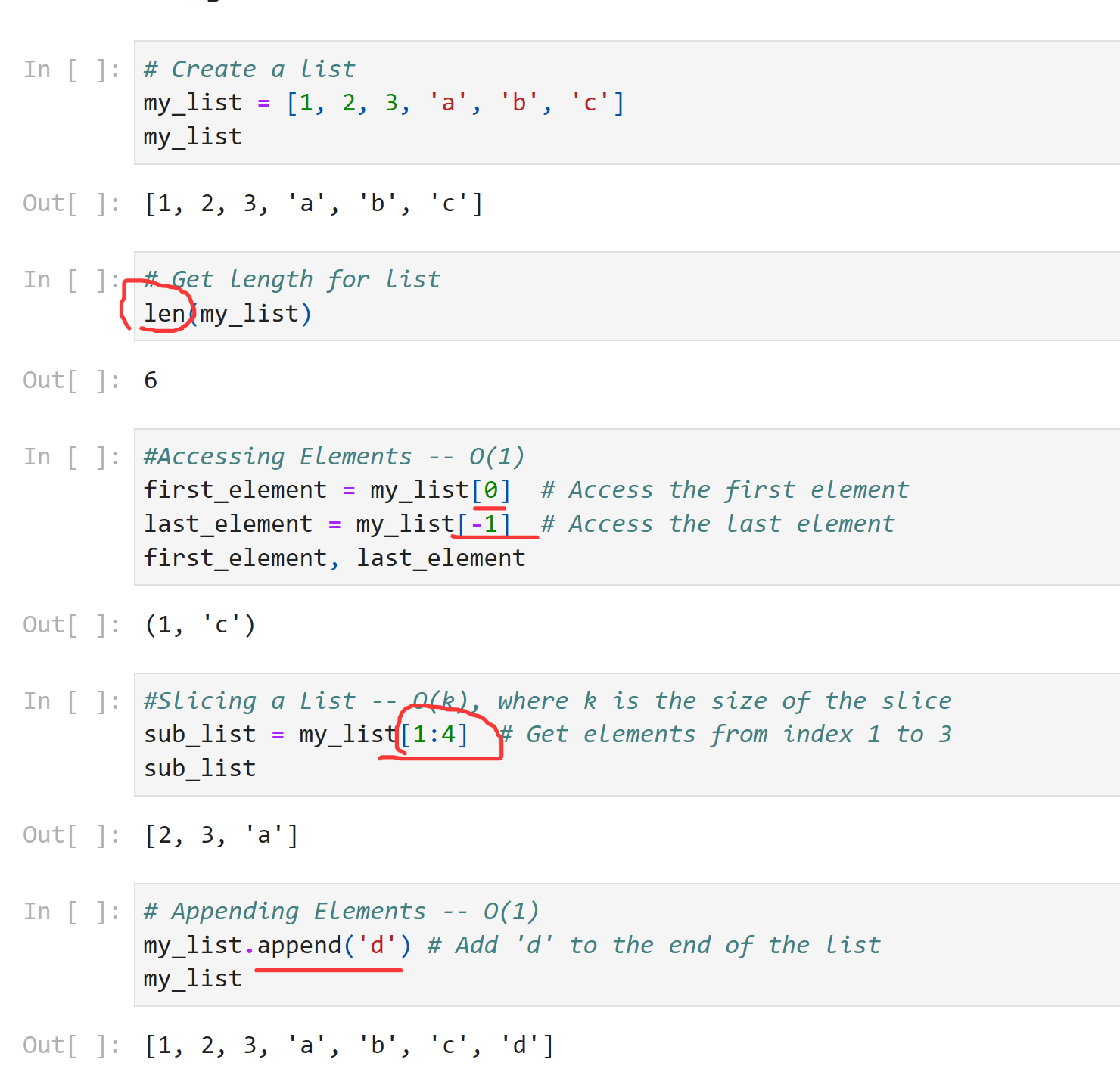
# Create a list my_list = [1, 2, 3, 'a', 'b', 'c'] my_list
Out[ ]:
[1, 2, 3, 'a', 'b', 'c']
In [ ]:
# Get length for list len(my_list)
Out[ ]:
6
In [ ]:
#Accessing Elements -- O(1) first_element = my_list[0] # Access the first element last_element = my_list[-1] # Access the last element first_element, last_element
Out[ ]:
(1, 'c')
In [ ]:
#Slicing a List -- O(k), where k is the size of the slice sub_list = my_list[1:4] # Get elements from index 1 to 3 sub_list
Out[ ]:
[2, 3, 'a']
In [ ]:
# Appending Elements -- O(1)
my_list.append('d') # Add 'd' to the end of the list
my_list
Out[ ]:
[1, 2, 3, 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd']
In [ ]:
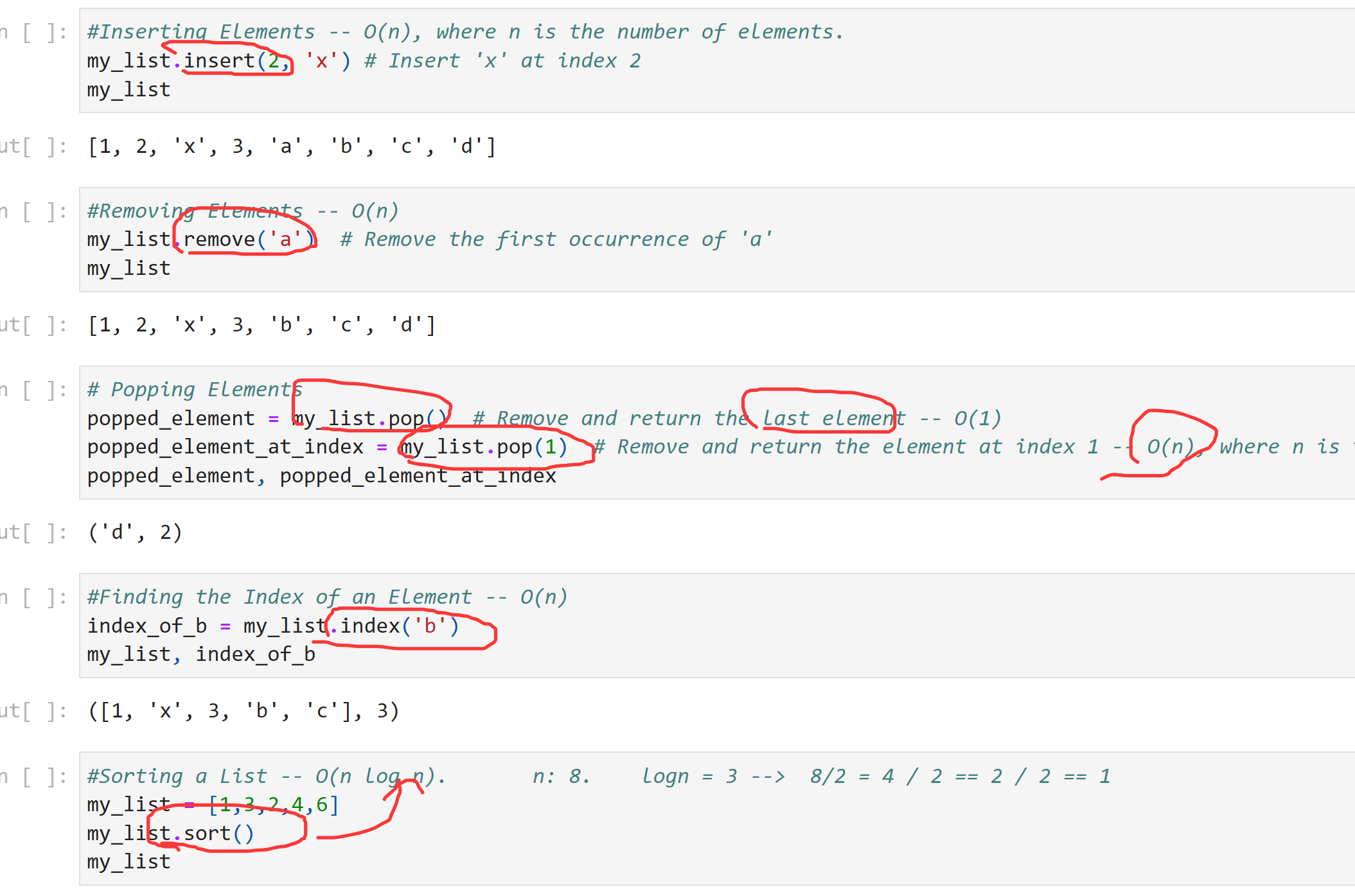
#Inserting Elements -- O(n), where n is the number of elements. my_list.insert(2, 'x') # Insert 'x' at index 2 my_list
Out[ ]:
[1, 2, 'x', 3, 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd']
In [ ]:
#Removing Elements -- O(n)
my_list.remove('a') # Remove the first occurrence of 'a'
my_list
Out[ ]:
[1, 2, 'x', 3, 'b', 'c', 'd']
In [ ]:
# Popping Elements popped_element = my_list.pop() # Remove and return the last element -- O(1) popped_element_at_index = my_list.pop(1) # Remove and return the element at index 1 -- O(n), where n is the number of elements after the popped index popped_element, popped_element_at_index
Out[ ]:
('d', 2)
In [ ]:
#Finding the Index of an Element -- O(n)
index_of_b = my_list.index('b')
my_list, index_of_b
Out[ ]:
([1, 'x', 3, 'b', 'c'], 3)
In [ ]:
#Sorting a List -- O(n log n). n: 8. logn = 3 --> 8/2 = 4 / 2 == 2 / 2 == 1 my_list = [1,3,2,4,6] my_list.sort() my_list
Out[ ]:
[1, 2, 3, 4, 6]
In [ ]:
# List Comprehension squared_numbers = [x**2 for x in range(10)] # O(n), where n is the length of the list squared_numbersa = [] for i in range(10):a.append(i ** 2) a, squared_numbers
Out[ ]:
([0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49,
Tuple
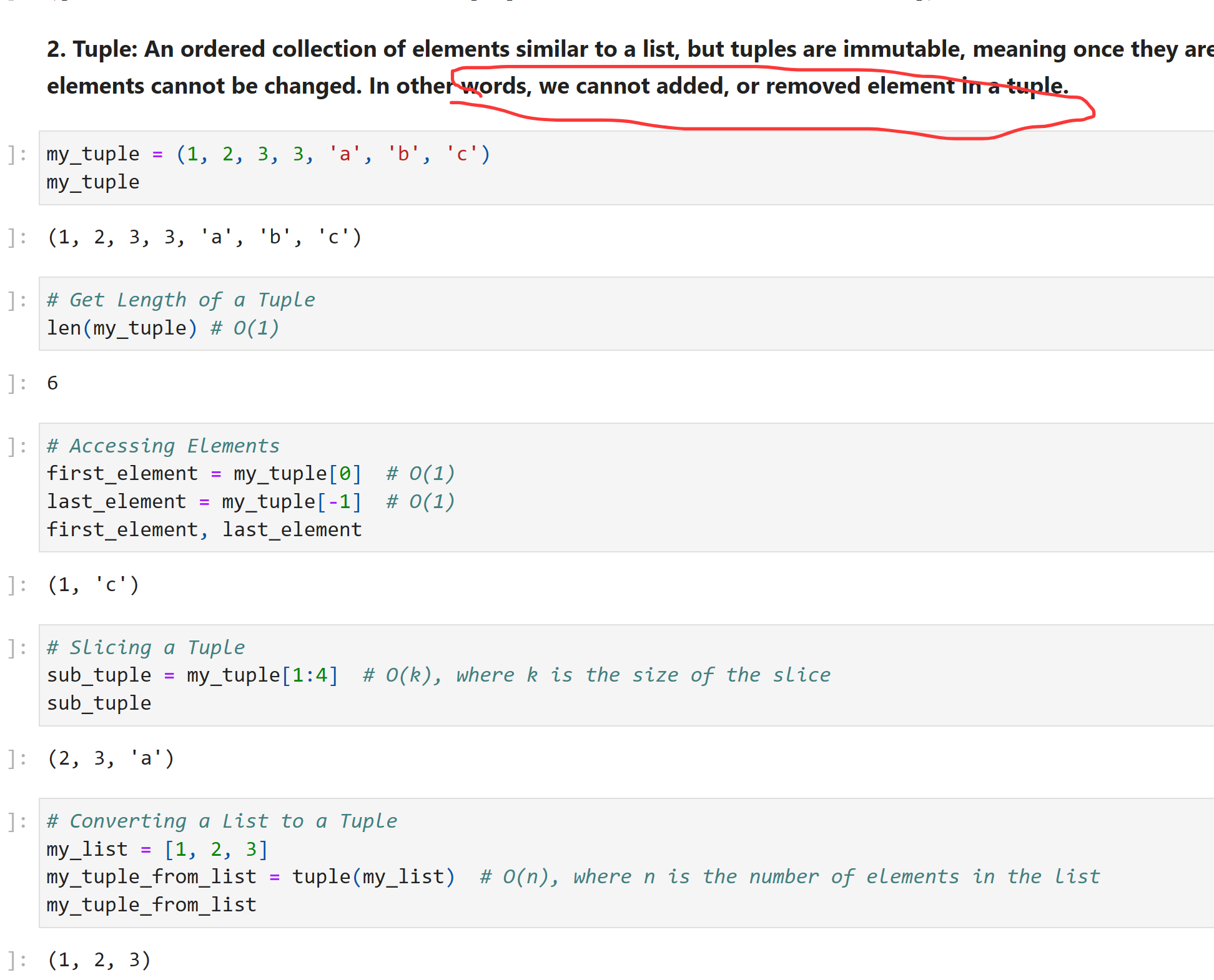
my_tuple = (1, 2, 3, 3, 'a', 'b', 'c') my_tuple
Out[ ]:
(1, 2, 3, 3, 'a', 'b', 'c')
In [ ]:
# Get Length of a Tuple len(my_tuple) # O(1)
Out[ ]:
6
In [ ]:
# Accessing Elements first_element = my_tuple[0] # O(1) last_element = my_tuple[-1] # O(1) first_element, last_element
Out[ ]:
(1, 'c')
In [ ]:
# Slicing a Tuple sub_tuple = my_tuple[1:4] # O(k), where k is the size of the slice sub_tuple
Out[ ]:
(2, 3, 'a')
In [ ]:
# Converting a List to a Tuple my_list = [1, 2, 3] my_tuple_from_list = tuple(my_list) # O(n), where n is the number of elements in the list my_tuple_from_list
Out[ ]:
(1, 2, 3)
In [ ]:
# Finding the Index of an Element
index_of_b = my_tuple.index('b') # O(n), where n is the number of elements
my_tuple, index_of_b
Out[ ]:
((1, 2, 3, 'a', 'b', 'c'), 4)
In [ ]:
# Counting Elements count_of_2 = my_tuple.count(2) # O(n), where n is the number of elements count_of_2
Out[ ]:
1
Tuple 与list的区别

Dict
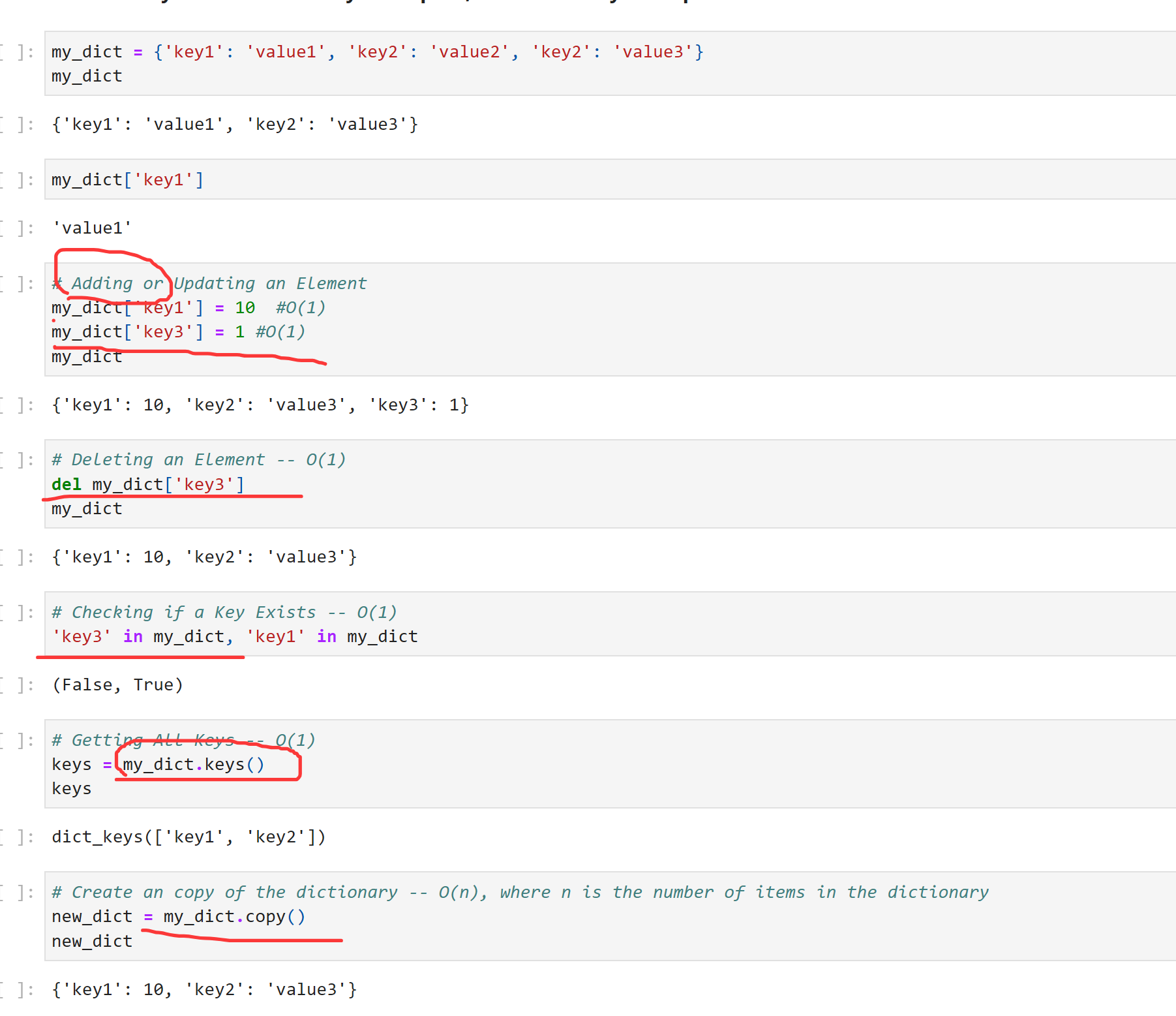
dict的遍历:
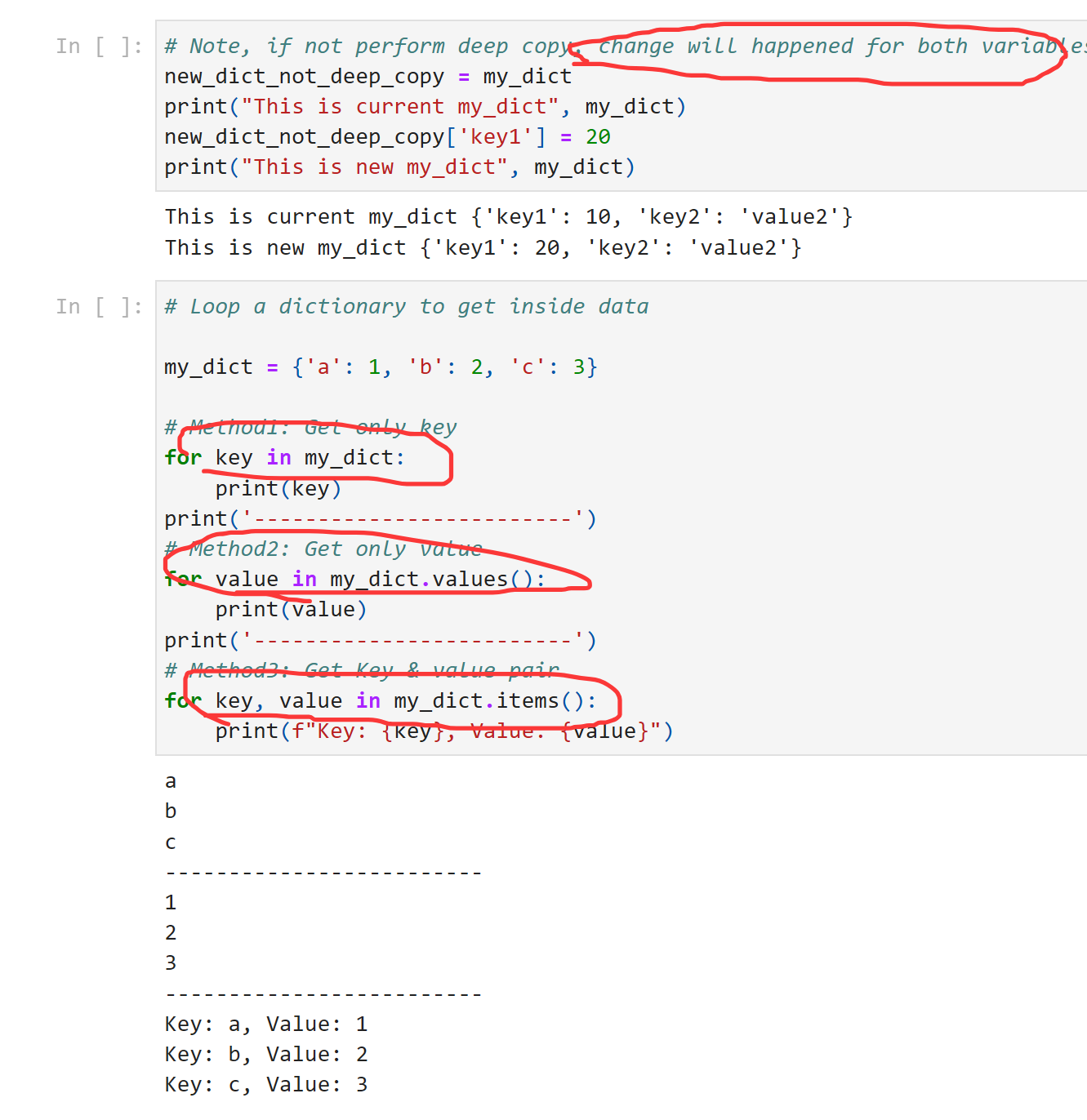
Set
set可以并集
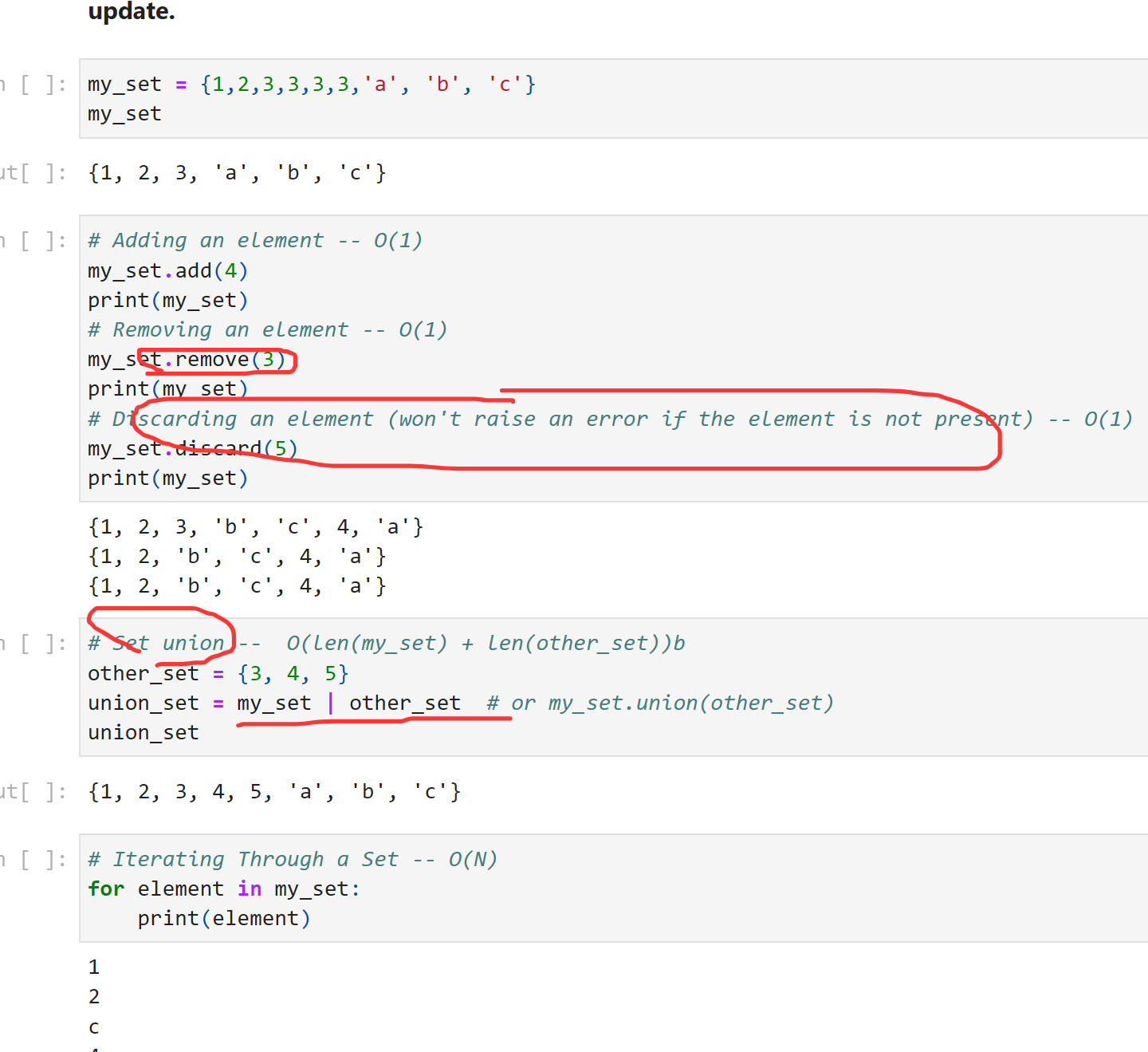
几个容器的比较
What is difference between dictionary and sets, when to use which?
Answer:
-
Structure
-
Dictionaries: Key-value pairs enclosed in curly braces {}.
-
Sets: Unique elements enclosed in curly braces {}.
-
-
Orders
-
Dictionaries: Maintain order of insertion (from Python 3.7 onwards).
-
Sets: Do not maintain any specific order.
-
-
Mutability:
-
Dictionaries: Both keys and values can be changed.
-
Sets: The set itself is mutable, but elements must be immutable.
-
-
Use Cases:
-
Dictionaries: Storing associated data, fast lookup by key.
-
Sets: Storing unique items, membership testing (if customerID present)
-
High level comparsion for 4 different basic data structures: List, Tuple, Dictionary, Sets
-
Lists:
-
Ordered + mutable
-
When you need a collection with a specific order and the ability to change its elements.
-
-
Tuples:
-
Ordered + immutable
-
When you need a collection with a specific order and the assurance that its elements won't change.
-
-
Dictionaries:
-
Unorded (Python 3.7 before) + mutable
-
When you need to map unique keys to values and access them efficiently via keys
-
-
Sets:
-
Unordered + mutable (but immutable for elements, cannot update)
-
When you need to store unique items and perform membership testing or set operations.
-
