函数指针
函数指针的格式类似这样:
int (*POINTER_NAME)(int a, int b)值得区别一下三种声明的区别:
1、char *make_coolness(int awesome_levels)
2、char (*make_coolness)(int awesome_levels)
3、char *(*make_coolness)(int awesome_levels)
第一种是一个普通的函数声明,表示make_coolness是一个函数,它接受一个int类型的参数 awesome_levels,并返回一个char *类型的结果。它的含义是:这是一个函数,能够根据给定的awesome_levels生成并返回一个字符指针。
第二种是一个函数指针声明,它表示make_coolness是一个指针,指向一个接受int类型参数并返回char类型结果的函数。这意味着make_coolness本身是一个指向函数的指针,而不是直接的函数。
第三种与第二种类似,区别就是指向函数的返回类型的不同,指向一个接受int类型参数返回char* 类型结果的函数。
函数指针用于传递回调的例子:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>/** Our old friend die from ex17. */
void die(const char *message)
{if(errno) {perror(message);} else {printf("ERROR: %s\n", message);}exit(1);
}// a typedef creates a fake type, in this
// case for a function pointer
typedef int (*compare_cb)(int a, int b);/*** A classic bubble sort function that uses the* compare_cb to do the sorting.*/
int *bubble_sort(int *numbers, int count, compare_cb cmp)
{int temp = 0;int i = 0;int j = 0;int *target = malloc(count * sizeof(int));if(!target) die("Memory error.");memcpy(target, numbers, count * sizeof(int));for(i = 0; i < count; i++) {for(j = 0; j < count - 1; j++) {if(cmp(target[j], target[j+1]) > 0) {temp = target[j+1];target[j+1] = target[j];target[j] = temp;}}}return target;
}int sorted_order(int a, int b)
{return a - b;
}int reverse_order(int a, int b)
{return b - a;
}int strange_order(int a, int b)
{if(a == 0 || b == 0) {return 0;} else {return a % b;}
}/*** Used to test that we are sorting things correctly* by doing the sort and printing it out.*/
void test_sorting(int *numbers, int count, compare_cb cmp)
{int i = 0;int *sorted = bubble_sort(numbers, count, cmp);if(!sorted) die("Failed to sort as requested.");for(i = 0; i < count; i++) {printf("%d ", sorted[i]);}printf("\n");free(sorted);// 打印回调函数的地址unsigned char *data = (unsigned char *)cmp;for(i = 0; i < 25; i++) {printf("%02x:", data[i]);}printf("\n");
}int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{if(argc < 2) die("USAGE: ex18 4 3 1 5 6");int count = argc - 1;int i = 0;char **inputs = argv + 1;int *numbers = malloc(count * sizeof(int));if(!numbers) die("Memory error.");for(i = 0; i < count; i++) {numbers[i] = atoi(inputs[i]);}test_sorting(numbers, count, sorted_order);test_sorting(numbers, count, reverse_order);test_sorting(numbers, count, strange_order);free(numbers);return 0;
}其中:
typedef int (*compare_cb)(int a, int b);只是定义了一个类型 compare_cb,该类型表示指向一个接受两个 int 参数并返回一个 int 的函数的指针。
void test_sorting(int *numbers, int count, compare_cb cmp)
{...
}int *bubble_sort(int *numbers, int count, compare_cb cmp){...
} 结合typedef传递函数地址,它不会创建新的类型,而是为已经存在的类型提供一个新的名字,简化代码的可读性和可维护性。
例如:
typedef int (*compare_cb)(int a, int b);int ascending(int a, int b) {return a - b;
}int descending(int a, int b) {return b - a;
}int main() {compare_cb cmp = ascending; // 使用别名声明函数指针printf("%d\n", cmp(3, 2)); // 调用函数
}
typedef语法为:
typedef existing_type new_type_name;
// 可以分离为俩段// 例如:
// example1:
typedef struct {int x;int y;
} Point;Point p1; // 相当于 struct Point p1;// example2:
typedef int (*compare_cb)(int a, int b);
compare_cb cmp = ascending; - 用十六进制编辑器打开
ex18,接着找到函数起始处的十六进制代码序列,看看是否能在原始程序中找到函数。
使用xxd命令以16进制打印出ex18的机器码内容:$ xxd ex18 | grep "..."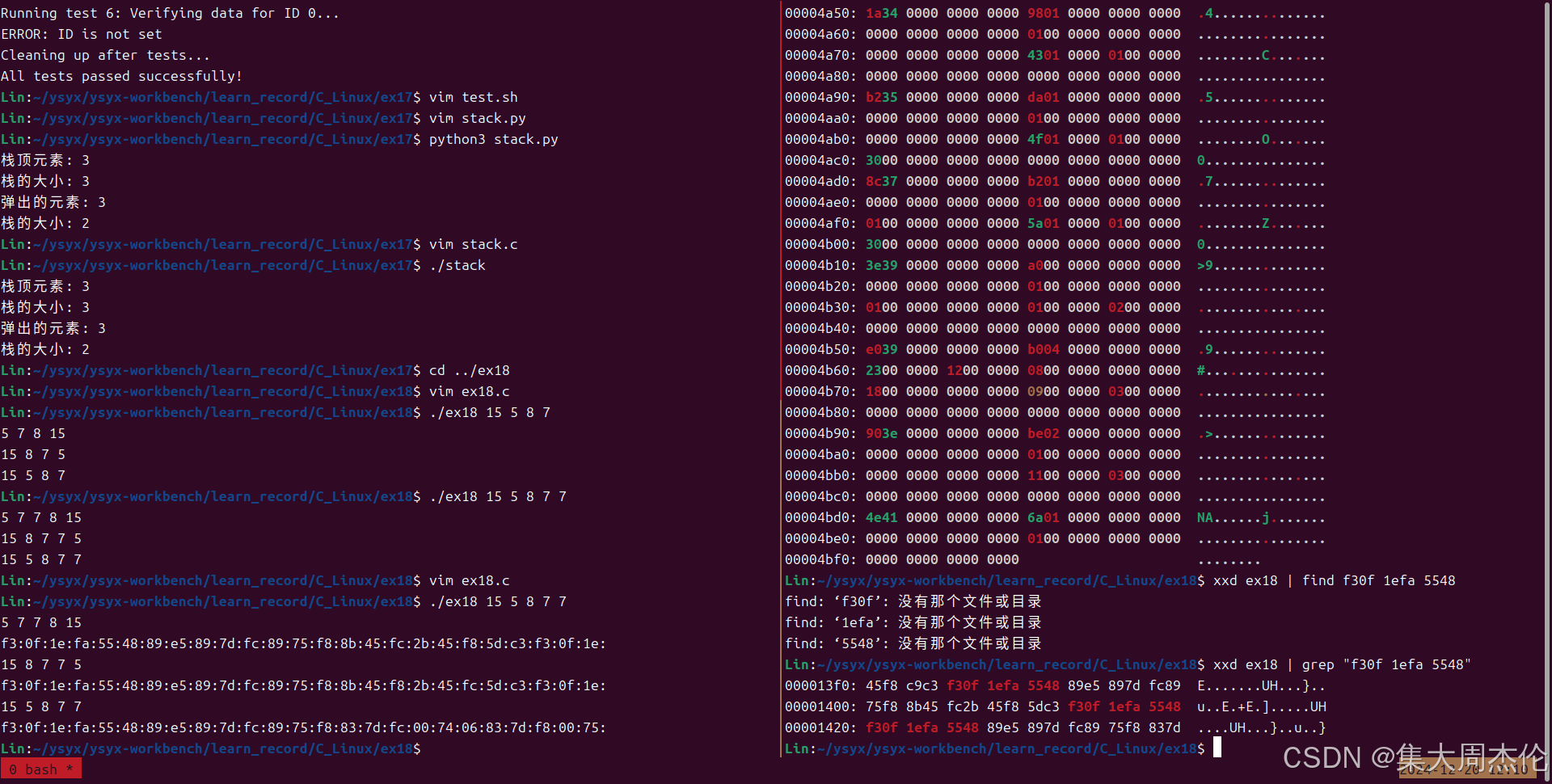
- 在你的十六进制编辑器中找到更多随机出现的东西并修改它们。重新运行你的程序看看发生了什么。字符串是你最容易修改的东西。
我们找到main函数中的一段字符串进行修改测试:
用vim编辑器打开并且输入":%!xxd"以16进制显示,然后查找到相应行处:if(argc < 2) die("USAGE: ex18 4 3 1 5 6"); // "USAGE: ex18 4 3 1 5 6"十六进制形式为:55 53 41 47 45 3A 20 65 78 31 38 20 34 20 33 20 31 20 35 20 36 00 // 找到对应的行内容为 00002040: 3278 3a00 5553 4147 453a 2065 7831 3820 2x:.USAGE: ex18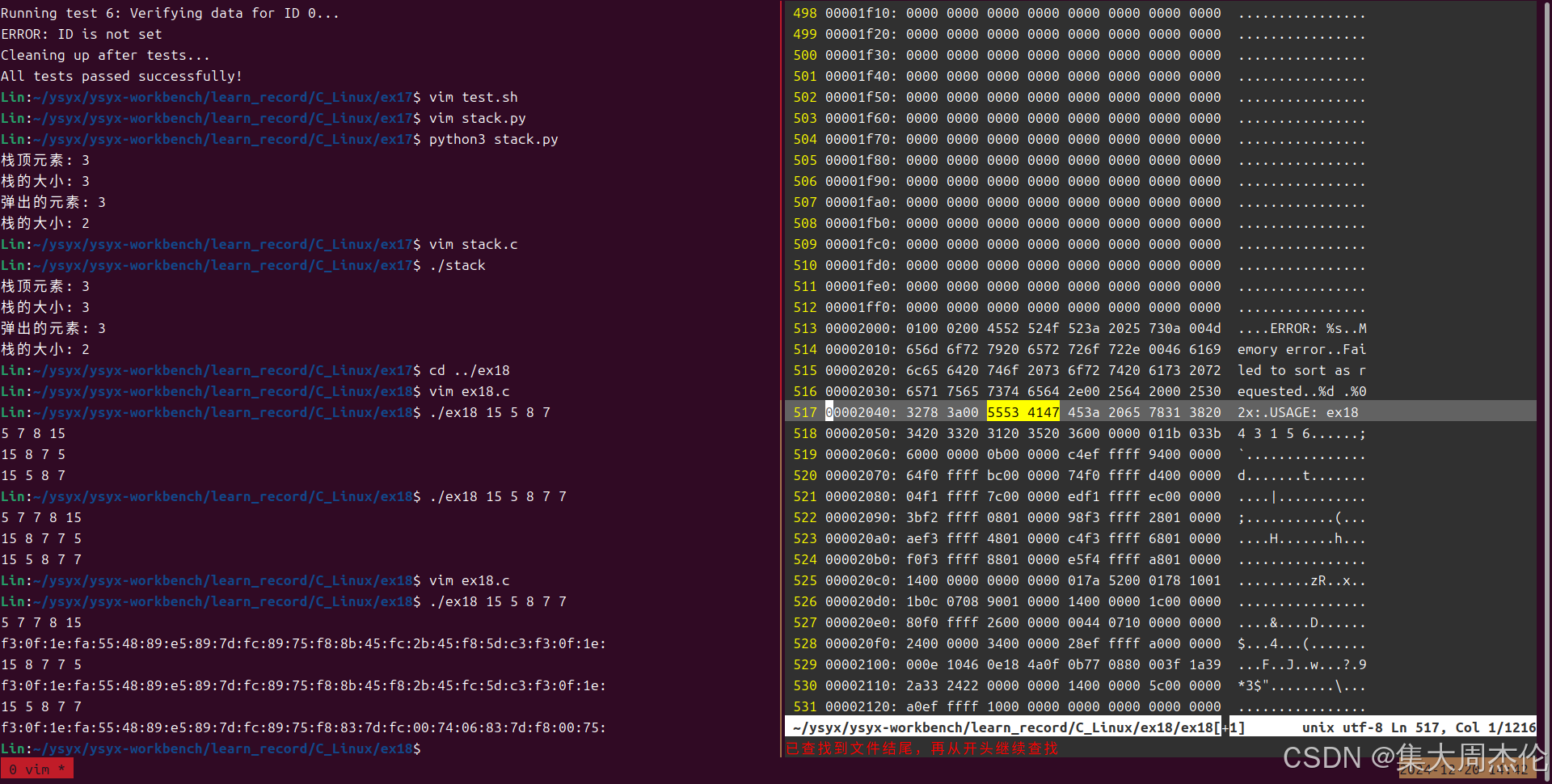
我们将USAGE改成小写的usage:
结果如下:U -> 85 (0x55) S -> 83 (0x53) A -> 65 (0x41) G -> 71 (0x47) E -> 69 (0x45) 改为: u -> 117 (0x75) s -> 115 (0x73) a -> 97 (0x61) g -> 103 (0x67) e -> 101 (0x65)
- 将错误的函数传给
compare_cb,并看看C编辑器会报告什么错误。 - 将
NULL传给它,看看程序中会发生什么。然后运行Valgrind来看看它会报告什么。$ valgrind ./ex18 4 6 7 9 5 3 ==6470== Memcheck, a memory error detector ==6470== Copyright (C) 2002-2024, and GNU GPL'd, by Julian Seward et al. ==6470== Using Valgrind-3.24.0 and LibVEX; rerun with -h for copyright info ==6470== Command: ./ex18 4 6 7 9 5 3 ==6470== ==6470== Jump to the invalid address stated on the next line ==6470== at 0x0: ??? ==6470== by 0x10947E: test_sorting (ex18.c:76) ==6470== by 0x109612: main (ex18.c:113) ==6470== Address 0x0 is not stack'd, malloc'd or (recently) free'd ==6470== ==6470== ==6470== Process terminating with default action of signal 11 (SIGSEGV) ==6470== Bad permissions for mapped region at address 0x0 ==6470== at 0x0: ??? ==6470== by 0x10947E: test_sorting (ex18.c:76) ==6470== by 0x109612: main (ex18.c:113) ==6470== ==6470== HEAP SUMMARY: ==6470== in use at exit: 48 bytes in 2 blocks ==6470== total heap usage: 2 allocs, 0 frees, 48 bytes allocated ==6470== ==6470== LEAK SUMMARY: ==6470== definitely lost: 0 bytes in 0 blocks ==6470== indirectly lost: 0 bytes in 0 blocks ==6470== possibly lost: 0 bytes in 0 blocks ==6470== still reachable: 48 bytes in 2 blocks ==6470== suppressed: 0 bytes in 0 blocks ==6470== Rerun with --leak-check=full to see details of leaked memory ==6470== ==6470== For lists of detected and suppressed errors, rerun with: -s ==6470== ERROR SUMMARY: 1 errors from 1 contexts (suppressed: 0 from 0) 段错误 (核心已转储)报告了Jump to the invalid address stated on the next line at 0x0: ???(提示在程序执行的下一行跳转到了无效的地址)以及 Address 0x0 is not stack'd, malloc'd or (recently) free'd(0x00地址不是栈也不是堆或者最近已经释放的内存地址)、 Bad permissions for mapped region at address 0x0(0x00地址映射区域限权错误)
- 编写另一个排序算法,修改
test_sorting使它接收任意的排序函数和排序函数的比较回调。并使用它来测试两种排序算法。/*插入排序算法*/ int *insertion_sort(int *numbers, int count, compare_cb cmp) {int i, j, temp;int *target = malloc(count * sizeof(int));if(!target) die("Memory error.");memcpy(target, numbers, count * sizeof(int));for(i = 1; i < count; i++) {temp = target[i];j = i - 1;while(j >= 0 && cmp(target[j], temp) > 0) {target[j + 1] = target[j];j = j - 1;}target[j + 1] = temp;}return target; }// 修改test_sorting函数 void test_sorting(int *numbers, int count, compare_cb cmp, int *(*sort_function)(int *, int, compare_cb)) {int i = 0;int *sorted = sort_function(numbers, count, cmp);if(!sorted) die("Failed to sort as requested.");for(i = 0; i < count; i++) {printf("%d ", sorted[i]);}printf("\n");free(sorted);// 打印回调函数的地址unsigned char *data = (unsigned char *)cmp;for(i = 0; i < 25; i++) {printf("%02x:", data[i]);}printf("\n"); }main函数中添加:
// 测试排序算法printf("Bubble Sort (Sorted Order):\n");test_sorting(numbers, count, sorted_order, bubble_sort);printf("Bubble Sort (Reverse Order):\n");test_sorting(numbers, count, reverse_order, bubble_sort);printf("Bubble Sort (Strange Order):\n");test_sorting(numbers, count, strange_order, bubble_sort);printf("Insertion Sort (Sorted Order):\n");test_sorting(numbers, count, sorted_order, insertion_sort);printf("Insertion Sort (Reverse Order):\n");test_sorting(numbers, count, reverse_order, insertion_sort);printf("Insertion Sort (Strange Order):\n");test_sorting(numbers, count, strange_order, insertion_sort);
